Benefits of efficient ITSM processes
Irrespective of the size of business, every organization is involved in IT service management in some way. ITSM ensures that incidents, service requests, problems,changes, and IT assets in addition to other aspects of IT services are managed in a streamlined way.
IT teams in your organization can employ various workflows and best practices in ITSM, as outlined in various industry standards.
Effective ITSM processes can have positive effects on an IT organization’s overall function.
Here are the 10 key benefits of ITSM:
- Lower costs for IT operations
- Higher returns on IT investments
- Minimal service outages
- Ability to establish well-defined, repeatable, and manageable IT processes
- Efficient analysis of IT problems to reduce repeat incidents
- Improved efficiency of IT help desk teams
- Well-defined roles and responsibilities
- Clear expectations on service levels and service availability
- Risk-free implementation of IT changes
- Better transparency into IT processes and services


IT service management (ITSM)?
IT Service Management (ITSM) refers to the practices, policies, and processes used by organizations to design, deliver, manage, and improve the way IT services are provided. It focuses on aligning IT services with business objectives and ensuring efficient, reliable, and high-quality service delivery to customers. ITSM encompasses a range of activities such as incident management (resolving disruptions in service), problem management (identifying root causes of issues), change management (managing IT changes to prevent service disruptions), and service level management (defining and monitoring service quality expectations). ITSM frameworks like ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) provide best practices for managing IT services in a structured manner. By implementing ITSM, organizations aim to improve service efficiency, reduce downtime, enhance customer satisfaction, and ensure continuous service improvement, all while maintaining compliance with industry standards and regulatory requirements.
ITSM processes
IT Service Management (ITSM) involves a set of structured processes that help organizations efficiently manage IT services and ensure they meet business objectives. Some key ITSM processes include:
Incident Management: This process focuses on restoring normal service operations as quickly as possible after an unplanned disruption or incident. It minimizes downtime and ensures that IT services are operational.
Problem Management: Aimed at identifying and addressing the root causes of incidents to prevent future occurrences. Problem management seeks long-term solutions rather than temporary fixes.
Change Management: This process manages changes to IT services or infrastructure, ensuring they are made in a controlled and systematic manner to prevent disruptions. Changes are assessed, approved, and implemented in a structured way.
Service Desk: The service desk acts as a single point of contact between users and IT, handling incidents, requests, and general inquiries. It ensures efficient communication and service delivery.
Service Level Management (SLM): This process defines and manages service level agreements (SLAs) between IT and business stakeholders. It ensures that IT services meet agreed-upon performance standards.
Configuration Management: It involves maintaining an up-to-date record of all IT assets and their relationships, ensuring that all configurations are properly managed and tracked.
Continuous Service Improvement (CSI): Focused on improving the effectiveness and efficiency of IT services over time, based on metrics, audits, and user feedback.
These processes ensure that IT services are aligned with business needs and are delivered effectively and efficiently.
Service design
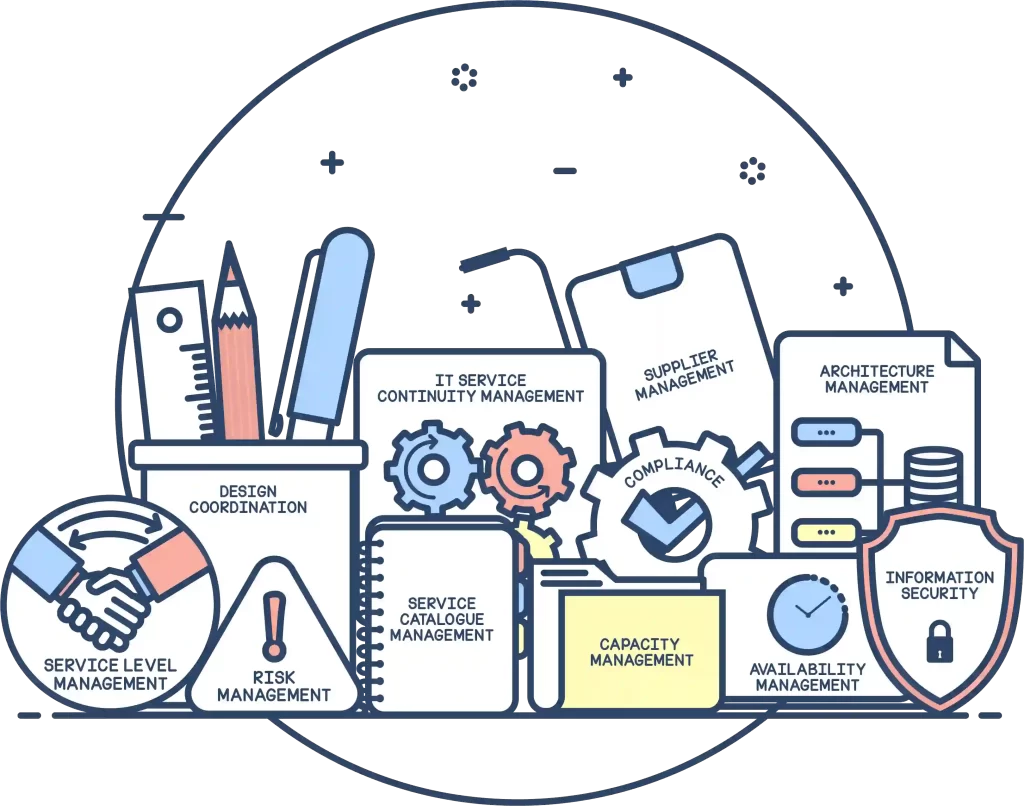
This stage’s main aim is planning and designing the IT services the organization offers to meet business demands. It involves creating and designing new services as well as assessing current services and making relevant improvements. There are several elements to IT service design:
Design coordination
Managing designs to ensure that the newly designed or modified services, information systems, technology, and metrics are consistent and effective.
Service catalogue management
Creating and maintaining a service catalog that provides all information pertaining to the organization’s IT offerings, their present status, and interdependencies.
Risk management
Identifying potential risks caused by IT service processes, recording them with their impact and plausible workarounds.
Service level management
Defining service-level agreements based on discussions with the customers, to ensue that services are designed based on them.
Service transition
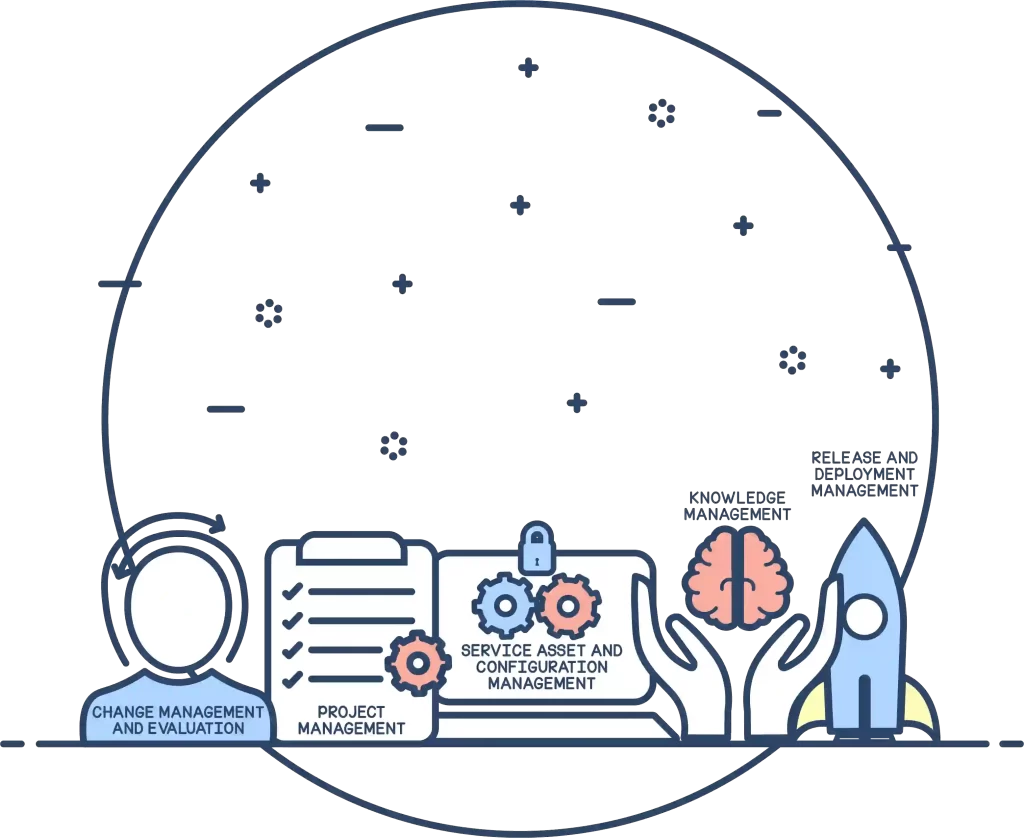
Once the designs for IT services and their processes have been finalized, it’s important to build them and test them out to ensure that processes flow. IT teams need to ensure that the designs don’t disrupt services in any way, especially when existing IT service processes are upgraded or redesigned. This calls for change management, evaluation, and risk management. No transition happens without risks and it’s important to be proactive during transitions.
Change management and evaluation
Controlling the life cycle of any IT change, including operational, strategic, or tactical changes.
Project management
Planning and managing major release activities.
Knowledge management
Maintaining a shared IT knowledge base within the organization.
Service asset and configuration Management
Maintaining and managing IT assets that are required for the offered IT services, and their configuration items (CIs).
Release and deployment management
Planning, scheduling, and controlling the deployment of various releases to ensure minimal disruption to existing services.
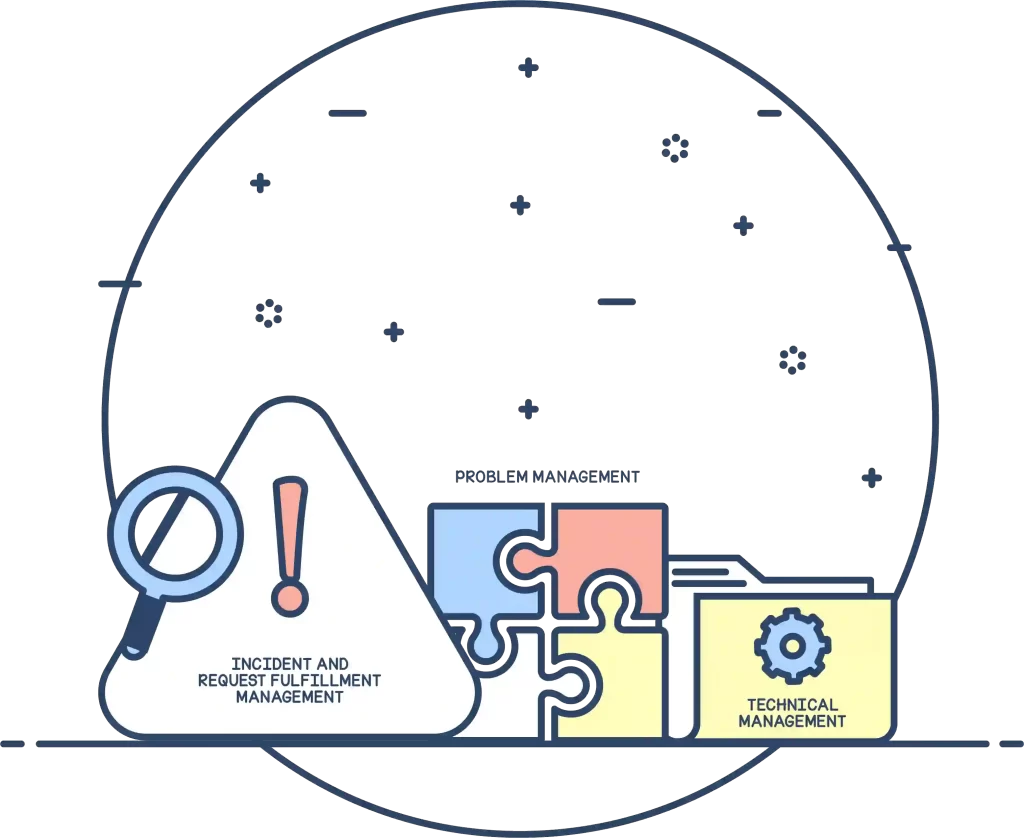
Service operation
This phase involves implementing the tried and tested new or modified designs in a live environment. While in this stage, the processes have already been tested and the issues fixed, but new processes are bound to have hiccups especially when customers start using the services. IT teams therefore need to closely monitor processes and workflows and be proactive in ensuring continuity in service delivery. The ITSM best practices define the following as some of the main processes in the service operation stage:
Incident and request fulfillment management
Ensuring that all IT incidents are resolved at the earliest and service requests are attended to within the agreed service level targets.
Problem management
Managing all IT problems, minimizing the impact of IT incidents that led to the problem, and coming up with a solution or a workaround.
Technical management
Managing the IT infrastructure with the most appropriate technical expertise and support.
How to effectively implement ITSM processes and workflows
The following steps are best practices that can help simplify the implementation and efficient use of ITSM processes and workflows:
Audit your current ITSM operations and identify the gaps
Before implementing ITSM processes in your organization, it’s best to identify your organization’s early goals and then work your way up. When it comes to implementing IT service management workflows, there’s no one-size-fits-all approach. Therefore, it’s important to carefully identify the areas of IT where ITSM processes can be; involve the right people; deploy the relevant technology; choose the right workflows; be aware of what’s at stake and the potential risks involved; and be prepared with strategies for recovery in circumstances where initiatives fall through the cracks.
Educate, communicate, and involve stakeholders while implementing ITSM processes
According to a McKinsey report, 70 percent of change projects fail because management is unable or unwilling to help employees embrace the change. To prevent this, your organization needs to create a culture that is receptive to change. This can be done by ensuring that all stakeholders are convinced about the benefits of strategizing and implementing good ITSM processes, and communicating with people outside the core implementation team through workshops, meetings, etc. to ensure that everyone involved is on the same page.
Outline the Critical Success Factors and keep tabs on KPIs and metrics
As the ITSM implementation progresses, your team needs to regularly monitor your IT help desk’s performance using metrics and KPIs to ensure continuous improvement. With the built-in reporting capability that ITSM tools offer, your team can generate various reports containing both high-level and granular data, aiding in performance analysis and decision-making. While it’s necessary to regularly analyze KPIs, the trick of the game is to measure the right metrics and KPIs for your help desk. This will help you avoid wasting time on irrelevant or insignificant metrics. Here are the most significant metrics and KPIs:

